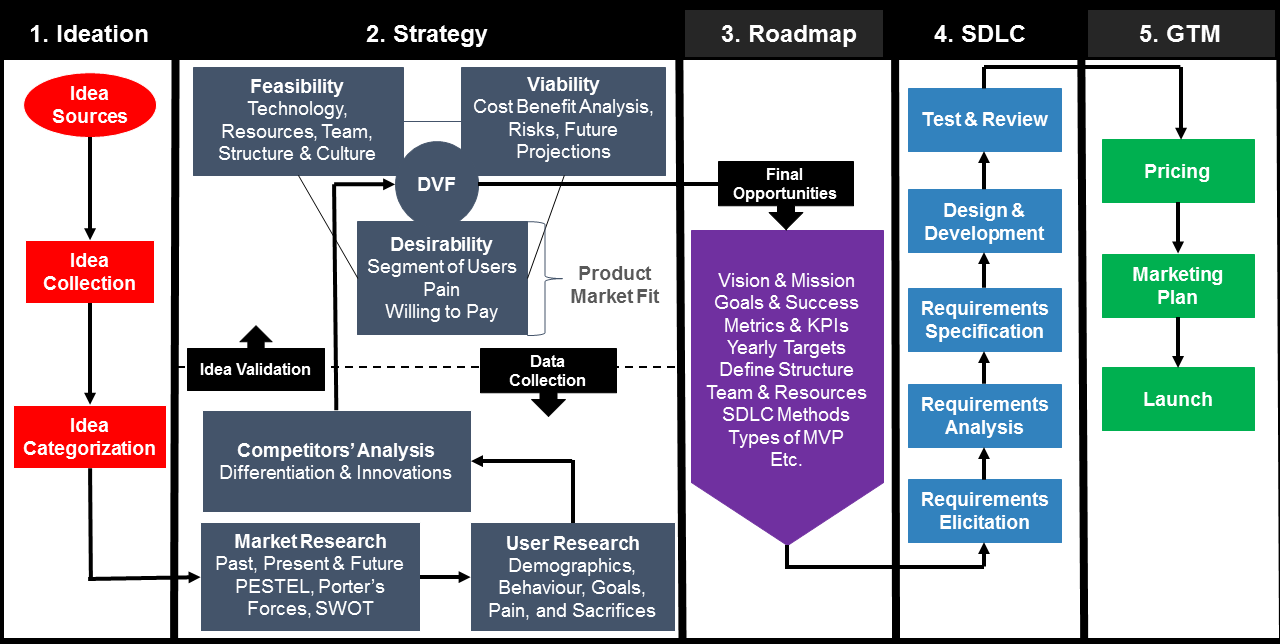
Steps in Product Design: From Concept to Launch
- By -Lepage Kathy
- Posted on
- Posted in Product Design
The journey from a product concept to its successful launch is a complex and multifaceted process that involves careful planning, creativity, technical expertise, and collaboration. Each stage is critical to ensuring that the final product meets user needs, performs as intended, and is ready for market introduction. This article outlines the essential steps involved in product design, from the initial concept to the final launch.
1. Concept Development
The first step in product design is developing the initial concept. This stage involves generating and refining ideas based on identified market needs and opportunities.
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to identify gaps, opportunities, and user needs. This includes analyzing competitors, understanding target demographics, and exploring trends.
- Brainstorming: Generate a wide range of ideas through brainstorming sessions, mind mapping, and other creative techniques. Encourage collaboration and open-minded thinking to explore all possibilities.
- Feasibility Study: Evaluate the feasibility of the concepts in terms of technical requirements, budget constraints, and market potential. Narrow down the ideas to those that are viable and promising.
2. Ideation and Concept Sketching
Once a viable concept is selected, the next step is to develop it further through detailed ideation and sketching.
- Concept Sketches: Create rough sketches to visualize the product’s form, function, and features. These sketches help in exploring different design directions and refining the concept.
- Mood Boards: Develop mood boards to gather visual inspiration and set the aesthetic tone for the product. This includes images, colors, materials, and textures that reflect the desired look and feel.
- Initial Prototypes: Build initial prototypes or mock-ups to test basic functionality and design assumptions. These prototypes can be simple and made from inexpensive materials.
3. Detailed Design and Development
With a clear concept in place, the detailed design and development phase begins. This stage involves creating comprehensive designs and specifications for the product.
- 3D Modeling: Use computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed 3D models of the product. These models provide a precise representation of the product’s dimensions, features, and components.
- Technical Drawings: Develop technical drawings and specifications that outline the product’s construction, materials, and manufacturing requirements. These documents serve as a blueprint for production.
- Material Selection: Choose appropriate materials based on functionality, aesthetics, cost, and sustainability considerations. Conduct material testing to ensure suitability.
4. Prototyping and Testing
Prototyping and testing are crucial for validating the design and ensuring that it meets user needs and performance standards.
- Functional Prototypes: Build functional prototypes that closely resemble the final product in terms of materials, features, and functionality. These prototypes allow for thorough testing and evaluation.
- Usability Testing: Conduct usability tests with target users to gather feedback on the product’s design, functionality, and user experience. Identify any issues and areas for improvement.
- Iterative Refinement: Use the feedback from testing to make necessary refinements to the design. This iterative process may involve multiple rounds of prototyping and testing.
5. Final Design and Production Planning
After refining the design through prototyping and testing, the final design is prepared for production.
- Final CAD Models and Specifications: Update the CAD models and technical specifications to reflect any changes made during the prototyping phase. Ensure all details are accurate and complete.
- Production Planning: Develop a detailed production plan that outlines the manufacturing process, timelines, and resources needed. Collaborate with manufacturers to ensure smooth production.
- Quality Assurance: Establish quality assurance protocols to ensure that the final product meets all performance, safety, and regulatory standards.
6. Pre-Launch and Marketing
Before launching the product, it is essential to prepare the market and create awareness among potential customers.
- Marketing Strategy: Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy that includes branding, positioning, pricing, and promotional activities. Identify the key messages and channels to reach the target audience.
- Packaging Design: Design attractive and functional packaging that protects the product and enhances its appeal. Ensure that the packaging communicates the product’s value proposition and brand identity.
- Pre-Launch Testing: Conduct final pre-launch testing to ensure that the product is ready for market introduction. This may include pilot production runs and field testing.
7. Product Launch
The product launch is the culmination of the design and development process. This stage involves introducing the product to the market and executing the launch plan.
- Launch Event: Plan and execute a launch event to generate excitement and media coverage. This can be a physical event, a virtual event, or a combination of both.
- Sales and Distribution: Implement the sales and distribution strategy to ensure that the product reaches the target market. This includes coordinating with retailers, distributors, and online platforms.
- Marketing Campaign: Roll out the marketing campaign to promote the product and drive sales. Use a mix of advertising, public relations, social media, and content marketing to reach potential customers.
8. Post-Launch Evaluation and Iteration
After the product is launched, it is essential to monitor its performance and gather feedback for continuous improvement.
- Performance Monitoring: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales, customer satisfaction, and market share. Use this data to evaluate the product’s success and identify areas for improvement.
- Customer Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and direct interactions. Use this feedback to address any issues and make iterative improvements.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously refine and improve the product based on user feedback and market trends. This may involve releasing updates, new features, or improved versions of the product.
Conclusion
The process of taking a product from concept to launch involves several critical steps that require careful planning, collaboration, and iteration. By following these steps, designers can ensure that their products are well-designed, functional, and ready for market success. Whether you are developing a new technology gadget, a piece of furniture, or a medical device, adhering to these stages will help you create products that meet user needs and stand out in the competitive marketplace.