Stages of Film Production: Bringing Cinematic Visions to Life
- By -Lepage Kathy
- Posted on
- Posted in Uncategorized
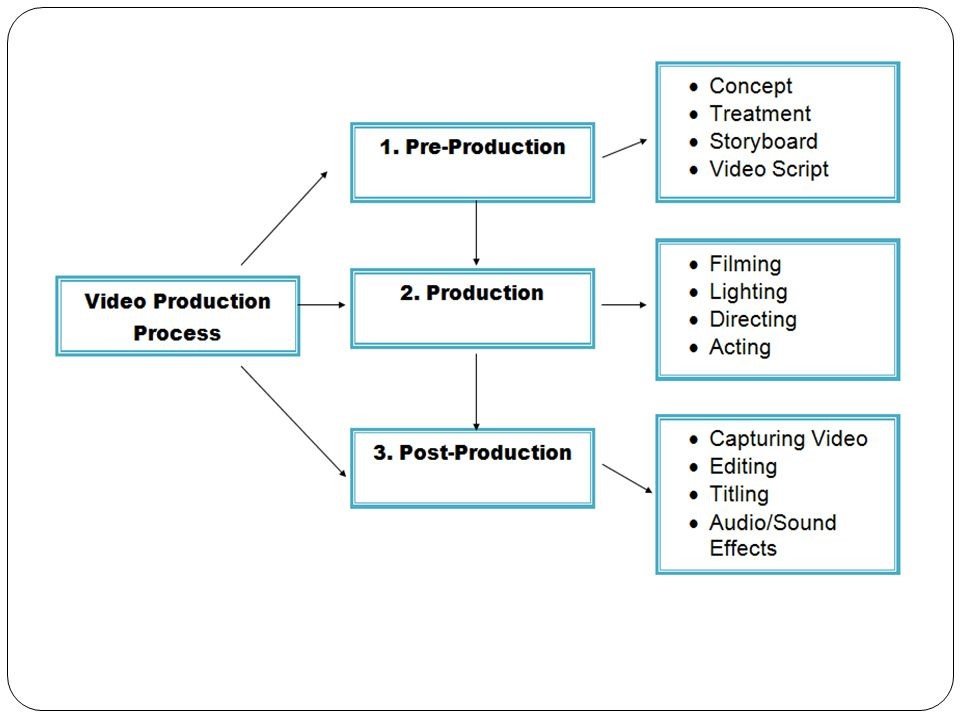
Film production is a multi-stage process that involves meticulous planning, creative execution, and technical expertise to transform ideas into compelling cinematic narratives. Each stage—pre-production, production, and post-production—plays a crucial role in shaping the visual, narrative, and emotional dimensions of a film, ensuring coherence, quality, and audience engagement.

Pre-Production: Planning and Preparation
Pre-production is the initial stage of filmmaking, where ideas are developed, scripts are finalized, and logistical arrangements are made to prepare for filming. Key activities include:
- Script Development: Writers refine the screenplay, incorporating feedback and revisions to establish the narrative structure and thematic elements.
- Casting: Directors and casting directors select actors and actresses who best embody the characters’ traits and motivations, ensuring a cohesive ensemble that brings the script to life.
- Location Scouting: Production teams identify and secure filming locations that align with the script’s setting and visual requirements, ensuring logistical feasibility and creative authenticity.
- Storyboarding and Shot Planning: Directors and cinematographers collaborate to visualize scenes through storyboards, outlining camera angles, framing, and visual compositions to guide filming.
- Budgeting and Scheduling: Producers manage financial resources and allocate budgets across various production elements, while scheduling outlines the sequence and timing of filming activities to optimize efficiency and meet deadlines.
Production: Filming and Performance
Production is the stage where principal photography takes place, with cast and crew coming together on set to capture scenes according to the script and storyboard. Key activities include:
- Direction and Performance: Directors guide actors in interpreting characters and delivering performances that align with the script’s emotional and narrative intentions, fostering creative collaboration and character development.
- Cinematography: Cinematographers oversee camera operations, lighting design, and visual composition to capture scenes that enhance mood, atmosphere, and thematic resonance, ensuring technical precision and artistic expression.
- Sound and Production Design: Sound engineers capture dialogue and ambient sounds, while production designers oversee set decoration, props, and costumes that enrich the film’s visual storytelling and immersive environment.
- Continuity and Logistics: Production assistants and coordinators manage logistics, ensuring continuity between scenes, coordinating cast and crew schedules, and addressing unforeseen challenges to maintain filming momentum and production efficiency.
Post-Production: Editing and Enhancement
Post-production is the final stage of film production, where raw footage is edited, refined, and enhanced to create a cohesive narrative and cinematic experience. Key activities include:
- Editing: Editors assemble footage, select shots, and refine sequences to achieve narrative coherence, pacing, and emotional impact, employing editing techniques such as continuity editing, montage, and sound synchronization.
- Visual Effects (VFX): VFX artists integrate computer-generated imagery (CGI), digital effects, and practical enhancements to augment visual storytelling, create immersive environments, and realize creative visions that transcend physical limitations.
- Sound Design and Mixing: Sound designers and mixers enhance auditory elements, incorporating dialogue, Foley effects, and musical scores to evoke atmosphere, emotion, and thematic resonance, ensuring balanced soundscapes and immersive auditory experiences.
- Color Grading and Finishing: Colorists adjust color palettes, contrast, and lighting nuances to establish visual mood, enhance cinematic aesthetics, and maintain stylistic consistency, ensuring visual coherence and thematic impact across scenes.
- Finalization and Distribution: Producers oversee final screenings, secure distribution deals, and coordinate marketing strategies to promote the film’s release, engaging audiences and maximizing exposure through theatrical, digital, and international distribution channels.
Collaborative Excellence and Artistic Achievement
Film production is a collaborative endeavor that combines artistic vision, technical expertise, and creative innovation to bring cinematic visions to life. Each stage—from pre-production planning and production execution to post-production refinement and distribution—represents a critical phase in realizing filmmakers’ creative ambitions and engaging audiences worldwide.
Conclusion
The stages of film production—pre-production, production, and post-production—underscore the dynamic process of transforming cinematic ideas into compelling narratives that resonate with audiences. By understanding the roles, responsibilities, and collaborative dynamics of each stage, filmmakers, scholars, and audiences alike gain insight into the artistry, craftsmanship, and cultural impact of filmmaking as a vibrant and evolving medium of artistic expression.