Setting Up Usability Tests: A Comprehensive Guide
- By -Lepage Kathy
- Posted on
- Posted in Product Design
Usability testing is a critical process for evaluating how easily users can interact with your product, website, or application. It helps identify issues, gather feedback, and improve the overall user experience. This guide will walk you through the steps to set up effective usability tests, from planning and preparation to execution and analysis.

1. Define the Objectives
Before conducting a usability test, it is essential to clearly define the objectives. What specific aspects of your product are you testing? Are you evaluating the overall user experience, specific functionalities, or particular design elements? Defining clear objectives helps you stay focused and measure success accurately.
2. Identify Your Target Users
Identify the target audience for your usability test. These users should represent your actual or potential customers who will interact with your product in real-world scenarios. Consider demographics, technical proficiency, and user behavior to ensure you have a representative sample. Recruiting participants can be done through various channels, such as customer databases, social media, or usability testing platforms.
3. Develop Test Scenarios and Tasks
Create realistic scenarios and tasks that participants will perform during the usability test. These scenarios should align with the objectives of your test and reflect common user goals. For example, if you are testing an e-commerce site, a task might be “Find and purchase a specific product.” Ensure that tasks are clear, concise, and achievable within a reasonable time frame.
4. Choose the Right Methodology
Select the most appropriate methodology for your usability test. There are several methods to choose from, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
- Moderated Usability Testing: A facilitator guides participants through the tasks, asks questions, and provides support if needed. This method allows for deeper insights but can be resource-intensive.
- Unmoderated Usability Testing: Participants complete the tasks on their own, typically using an online platform. This method is more scalable and cost-effective but offers less opportunity for real-time interaction.
- Remote Usability Testing: Participants perform tasks from their location, either moderated or unmoderated. This method is convenient and can reach a broader audience.
- In-Person Usability Testing: Participants come to a testing location and complete tasks under direct observation. This method provides rich insights but can be logistically challenging.
5. Prepare the Test Environment
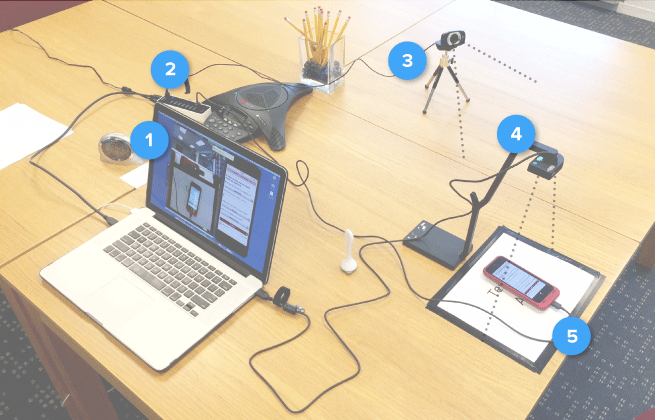
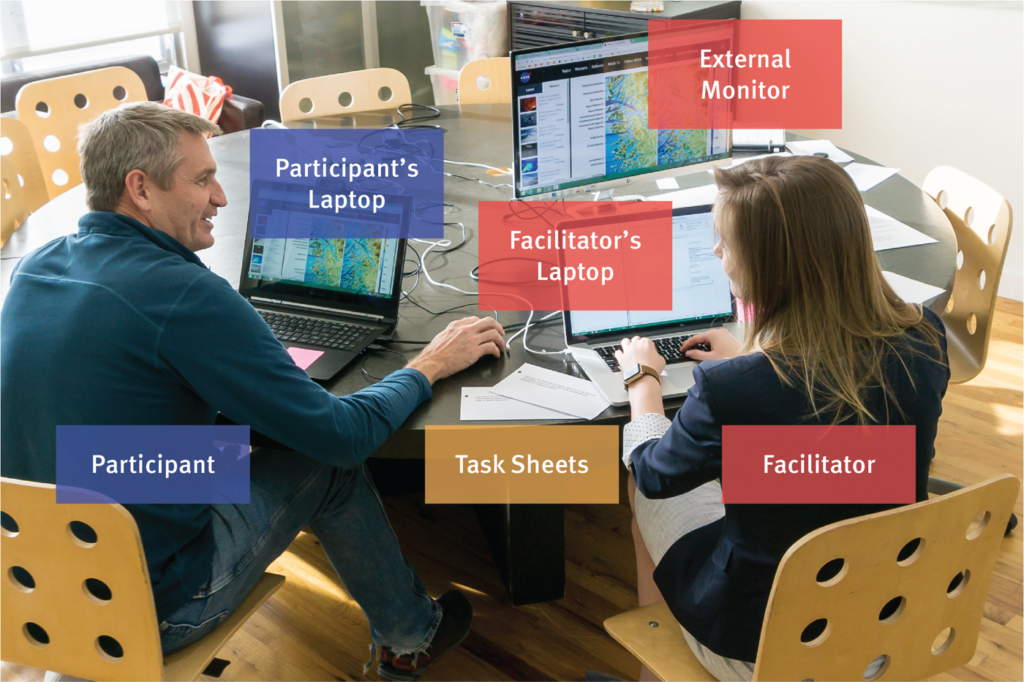
Set up a test environment that simulates real-world conditions as closely as possible. Ensure that the necessary equipment, such as computers, mobile devices, cameras, and recording software, is ready and functioning. If conducting remote tests, verify that participants have the required tools and software to participate. Make sure the environment is quiet and free from distractions to ensure accurate results.
6. Create a Test Script
Develop a test script to guide the usability test session. The script should include an introduction, instructions for each task, and any questions you want to ask participants. The introduction should explain the purpose of the test, assure participants that their performance is not being judged, and encourage them to think aloud as they complete the tasks. A well-structured script helps ensure consistency across sessions and provides a clear framework for facilitators.
7. Conduct a Pilot Test
Before conducting the full usability test, perform a pilot test with a small group of participants. The pilot test helps identify any issues with the test script, tasks, or equipment and allows you to make necessary adjustments. It also provides an opportunity to practice moderating and refine your approach.
8. Execute the Usability Test
During the usability test, follow the test script closely and observe participants as they complete the tasks. If conducting moderated tests, ask clarifying questions and encourage participants to verbalize their thoughts. Take detailed notes on participants’ behaviors, comments, and any difficulties they encounter. For unmoderated tests, ensure that the recording software captures all interactions for later analysis.
9. Analyze the Results
After completing the usability tests, analyze the data to identify patterns, common issues, and areas for improvement. Look for trends in participant behavior, recurring problems, and any deviations from expected outcomes. Categorize and prioritize issues based on their impact on the user experience and the frequency of occurrence. Use qualitative data, such as participant feedback, and quantitative data, such as task completion rates and time on task, to draw meaningful conclusions.
10. Report Findings and Recommend Changes
Create a comprehensive report that summarizes the findings from the usability tests. The report should include an overview of the objectives, methodology, participant demographics, key findings, and actionable recommendations. Use visuals such as charts, graphs, and screenshots to illustrate points and highlight significant issues. Share the report with stakeholders, including designers, developers, and product managers, and collaborate on implementing the recommended changes.
Conclusion
Setting up usability tests is a vital step in creating user-friendly products that meet the needs and expectations of your target audience. By defining clear objectives, identifying target users, developing realistic scenarios, choosing the right methodology, preparing the test environment, and analyzing the results, you can gain valuable insights and improve your product’s usability. Following these steps ensures that your usability testing process is thorough, effective, and ultimately beneficial to the user experience.